Community pruning is the method of bettering or simplifying a community by eradicating pointless or redundant components to enhance efficiency, effectivity and manageability. Listed here are some widespread community harvesting methods:
Community Harvesting Strategies
1. Harvesting of VTP
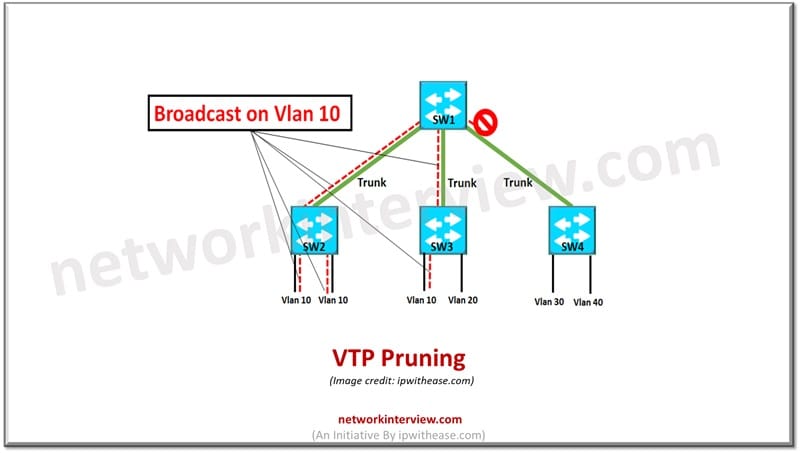
VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) pruning is used to cut back pointless VLAN site visitors on trunk hyperlinks in Cisco networks. This ensures that solely mandatory VLAN data is marketed throughout the community.
How does it work?
when Harvesting of VTP Enabled, a swap prevents broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast site visitors of VLANs from passing by way of trunk hyperlinks if downstream switches don’t have any ports assigned to these VLANs.
Benefits:
Reduces pointless site visitors and will increase out there bandwidth on trunk hyperlinks.
2. Path abstract
Often known as route aggregation, this method entails combining a number of IP routes right into a single abstract route to cut back the dimensions of the routing desk.
How does it work?
As an alternative of promoting a number of particular routes, routers promote a brief route that represents a number of subnets. This reduces the complexity of routing tables and reduces routing updates.
Benefits:
Simplifies routing tables, reduces CPU load on routers, and optimizes reminiscence utilization.
3. Pruning of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
STP pruning helps scale back the variety of energetic hyperlinks within the community whereas sustaining redundancy.
How does it work?
STP identifies redundant hyperlinks in a Layer 2 topology and locations some ports in a blocking state to stop loops. Lively forwarding paths are lower to create a loop-free community.
Benefits:
Reduces the prospect of broadcast storms and optimizes community topology.
4. Multicast harvesting
This entails limiting the distribution of multicast site visitors to solely these gadgets which might be serious about receiving the site visitors.
How does it work?
Protocols reminiscent of IGMP (Web Group Administration Protocol) and PIM (Protocol Unbiased Multicast) intercept multicast site visitors, making certain that it’s despatched solely to elements of the community the place there are receivers. .
Benefits:
Multicast conserves bandwidth by limiting site visitors to related elements of the community.
5. Firewalls and ACL pruning
Firewalls And entry management lists (ACLs) can be utilized to cut back pointless site visitors by blocking or proscribing sure forms of information.
How does it work?
By implementing strict firewall guidelines or ACLs, directors can prohibit sure site visitors (eg, ICMP requests, unused protocols) from passing by way of the community, lowering load and lowering safety dangers. from
Benefits:
Enhances safety, reduces pointless site visitors, and reduces community congestion.
6. Hyperlink Aggregation Management Protocol (LACP) harvesting
LACP is used to bind a number of bodily hyperlinks between switches right into a single logical hyperlink to extend bandwidth and supply redundancy.
How does it work?
By eradicating pointless or underutilized hyperlinks in a bundle, LACP can optimize a community by chopping inactive hyperlinks and conserving solely energetic ones.
Benefits:
Reduces the overhead of managing a number of particular person hyperlinks and ensures environment friendly use of accessible bandwidth.
7. Wi-fi community harvesting
This entails eradicating unused or out of date entry factors (APs) within the wi-fi community to enhance protection and scale back interference.
How does it work?
By conducting web site surveys and monitoring community utilization, directors can take away or disable APs that contribute little to total protection or efficiency.
Benefits:
Reduces community interference, improves efficiency, and simplifies community administration.
This community pruning method helps enhance community efficiency by eliminating redundant or pointless components, main to higher efficiency and extra streamlined administration.
Associated FAQs
Q.1 What’s community pruning in VLANs, and why is it essential?
Community pruning, particularly VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) pruning, is a technique of stopping pointless broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast site visitors on trunk hyperlinks of VLANs that aren’t actively used on these hyperlinks. are This optimizes bandwidth utilization, improves community efficiency, and reduces CPU load on gadgets.
Q.2 How does VTP trunking work in a community?
VTP pruning dynamically removes VLANs that shouldn’t have energetic hosts on downstream switches from trunk ports. The pruning course of makes use of VTP commercials to establish the VLANs which might be energetic on every swap. If a VLAN has no energetic members on the trunk, it’s dropped, stopping site visitors for that VLAN from passing by way of the trunk.
Q.3 What are the harvesting limits of VTP?
- Solely VLANs 2-1001 are affected: VTP pruning doesn’t harvest site visitors for VLAN 1 or prolonged VLANs (1006-4094).
- Handbook configuration is required: VTP logging have to be explicitly enabled and VTP doesn’t function in clear mode.
- Restricted to Cisco gadgets: VTP harvesting is a Cisco-specific function and doesn’t apply to gadgets from different distributors.
- Inter-VLAN site visitors: This doesn’t have an effect on inter-VLAN routing site visitors, which nonetheless traverses routed hyperlinks.
Q.4 How is VTP logging enabled on a swap?
To allow VTP logging:
- Be certain that the swap is on. VTP server or VTP Shopper mode (not clear).
- Use the command: swap (configuration)# Harvesting VTP
- Verify the harvest standing with: Change on.# Present VTP standing.
Search for the “VTP pruning” subject to substantiate it’s enabled.
Q.5 What are the perfect methods to make use of VTP logging?
- Allow solely when mandatory: Use VTP pruning in massive networks with many VLANs and trunk hyperlinks to keep away from pointless site visitors.
- Backup configuration: Earlier than enabling pruning, make sure that the VLAN database and swap configurations are backed up.
- Use the everlasting VTP model: Make sure that all collaborating switches use the identical VTP model to keep away from compatibility points.
- Monitor site visitors: Use monitoring instruments to confirm the impression of logging and confirm that reputable site visitors just isn’t inadvertently being logged.